Structure of Government
Government and its Arms
Lesson Objectives:
Describe the structure of the government- the principle of separation of powers.
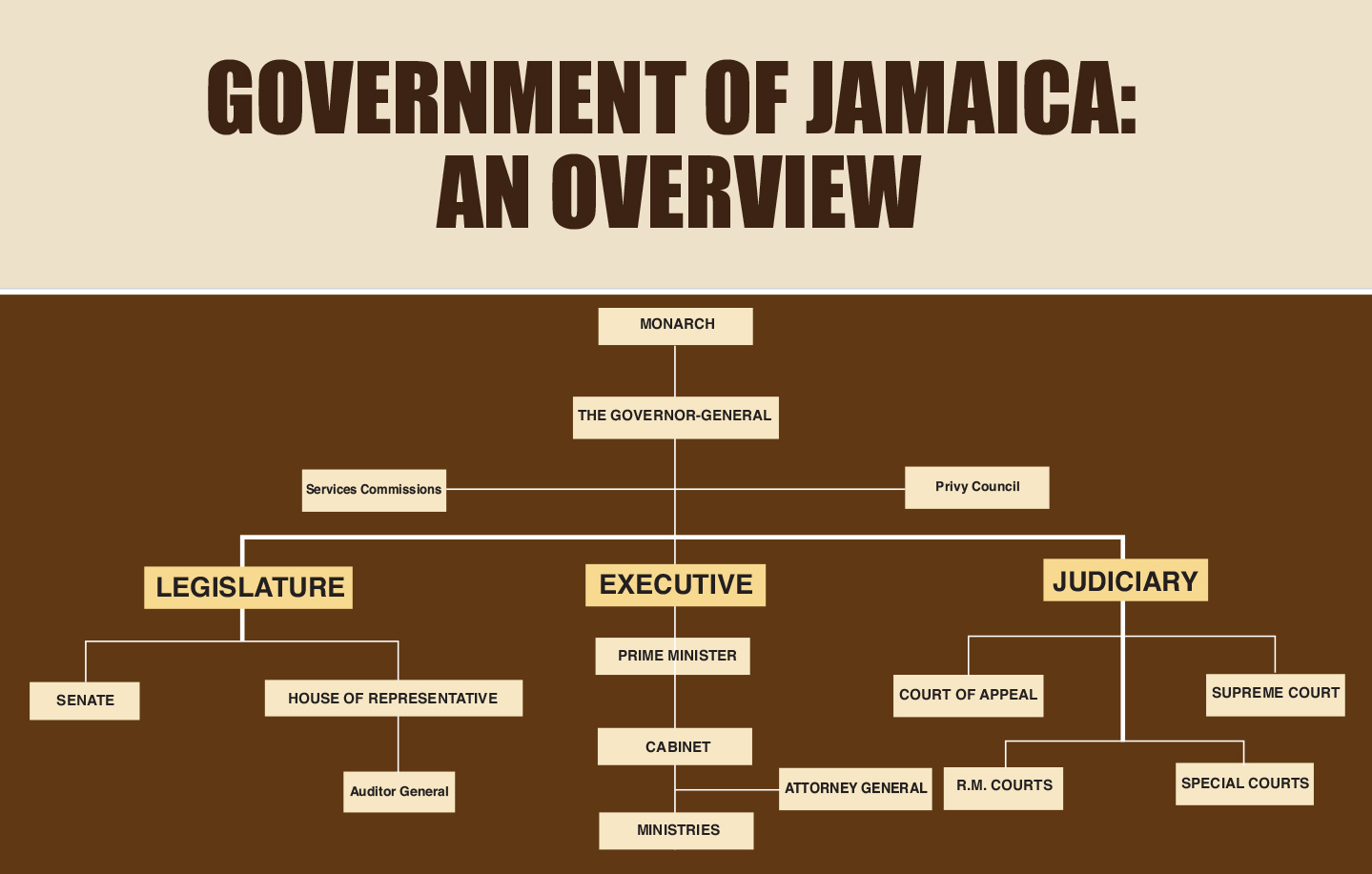
THE SEPARATION of powers doctrine ensures that the balance of power is maintained within each arm of the state. As it relates to Jamaica, separation of powers exists as there are safeguards put in place to ensure that no institution overpowers the other or usurp its function. The statement ‘separation of powers’ describes the distribution of power between different branches of government.
In most Caribbean countries, this is between the executive, judicial and legislative responsibilities of a government which, to a large extent, are separate and distinct bodies. It is widely believed that a separation of power would prevent the abuse of power by an individual or any single governmental body.
The system of governance in Jamaica is a constitutional monarchy under which the queen,
represented by a governor general, is head of state.
Under the constitutional monarchy, there are three arms of government:
The executive
The legislature
The judiciary
The Executive

THE EXECUTIVE in most Caribbean countries is based on the Westminster model of government, consisting of some of the elected members of parliament and appointed members of the Senate who form the Cabinet, headed by the prime minister. Some members of the civil service are also a part of the executive, such as the attorney general.

The Cabinet is the centre of the system of government. It initiates government policies and programmes and is responsible for the general direction and control of the Government. The Cabinet must consist of the prime minister and not less than 11 other ministers. Not more than four ministers must be appointed from the Senate, and they may have portfolio responsibilities.
The other Cabinet ministers are appointed from the House of Representatives. Cabinet ministers may be assisted by ministers of state (Junior Ministers. example. State Minister/Minister without a portfolio of Education) and parliamentary secretaries. However, important matters, especially those which may become the subject of discussion in Parliament, are brought before the Cabinet for
discussion and decision.
ROLE OF THE CABINET
To formulate policies to guide the growth and development of a country.
To decide on the Budget.
To make decisions about the internal and external affairs of the country.
To manage the day-to-day activities of the society.
To maintain proper security and defence for citizens.
To approve recommendations from various ministries.
To obtain loans from national, regional and international sources.
CABINET

The Cabinet is the centre of the system of government. It initiates government policies and programmes and is responsible for the general direction and control of the Government. The Cabinet must consist of the prime minister and not less than 11 other ministers. Not more than four ministers must be appointed from the Senate, and they may have portfolio responsibilities.
The other Cabinet ministers are appointed from the House of Representatives. Cabinet ministers may be assisted by ministers of state (Junior Ministers. example. State Minister/Minister without a portfolio of Education) and parliamentary secretaries. However, important matters, especially those which may become the subject of discussion in Parliament, are brought before the Cabinet for
discussion and decision.
ROLE OF THE CABINET
To formulate policies to guide the growth and development of a country.
To decide on the Budget.
To make decisions about the internal and external affairs of the country.
To manage the day-to-day activities of the society.
To maintain proper security and defence for citizens.
To approve recommendations from various ministries.
To obtain loans from national, regional and international sources.
THE CIVIL SERVICE

This refers to the body of employees in any government agency other than the military.
Referred to as civil servants or public servants, these individuals are employed in the public sector in/for a government department or agency.
The civil service executes government decisions and, therefore, plays a vital part in
politics. It is split into a number of departments attached to a government department.
Additionally, there are special bodies under Jamaican law with direct authority over certain
aspects of government business. These bodies are known as statutory bodies and are
autonomous agents within the Government of Jamaica hierarchy. Examples of statutory bodies
are the Jamaica National Heritage Trust and the National Housing Trust.

STRUCTURE OF THE LEGISLATIVE
The Parliament of Jamaica is the legislative branch of the Government of Jamaica. It is a
bicameral body, composed of an appointed Senate, also known as the Upper House, and an
elected House of Representatives, also known as the Lower house.
The governor general represents the queen in Parliament, and his role is a formal one. Once a
year, at the official opening of Parliament, he delivers the Throne Speech. The legislature is empowered by the Constitution to amend existing and enact new laws. This arm is also in control of the government’s finances and guides fiscal policy.
The head of state’s role in Parliament, executed through the governor general, is to open and dissolve Parliament and grant royal assent to bills passed in the Houses of Parliament.
SENATE
The Senate is a nominated house made up of 21 senators in Jamaica. Thirteen senators are appointed by the governor general on the advice of the prime minister. The other eight are appointed on the advice of the leader of the opposition. Not more than four ministers can be appointed from the Senate, and they may have portfolio responsibilities.

The Senate usually functions as a review chamber, considering bills passed by the House of Representatives. The Senate may also initiate legislation, except money bills.
The House of Representatives consists of 63 members, elected by single-member constituencies using the first-past-the-post system. The government in power can only exist if it has the support of the majority of the members of the House of Representatives. Most bills are initiated in the House of
Representatives.
THE SPEAKER

The Speaker of the House is formally elected by the members of the House of Representatives from among their number, at the first sitting after each general election or when there is a vacancy. His job includes keeping other members within the rules of the House, and ensuring that the rights of the opposition members are protected and that every member gets a fair hearing.
THE JUDICIARY
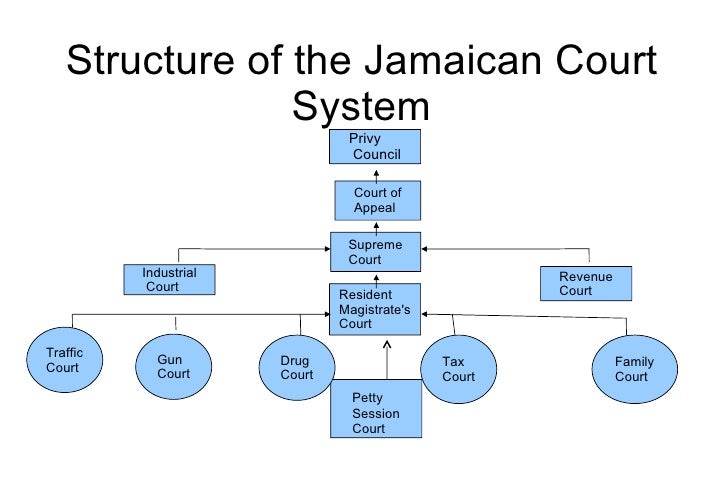
The legal system of Jamaica is based on British common law. The administration of justice is carried out through a court system.
The courts of Jamaica are:
The Judicial Committee of the Privy Council, which is the final court of appeal, is based in London, England. It hears appeals on criminal and civil matters from the Jamaican Court of Appeal.
 The fairly newly formed Caribbean Court of Justice (CCJ) is one of the primary institutions
The fairly newly formed Caribbean Court of Justice (CCJ) is one of the primary institutions
of the Caribbean Community (CARICOM). The CCJ has two core functions: to act as the final appellate court for the CARICOM member states and as an international court ruling on matters relating to the foreign policy coordination of the Revised Treaty of Chaguaramas (2001) that outlines terms of economic cooperation among CARICOM members.

The Court of Appeal consists of the resident of the Court of Appeal, the chief justice (who sits at the invitation of the president) and six judges of the Court of Appeal. A person who is dissatisfied with a decision of one of the other courts, except Petty Sessions, can appeal to this court. Petty Sessions appeals are heard by a judge in chambers or by justices of the peace.

The Supreme Court of Jamaica is responsible for hearing serious civil and criminal matters.
 Resident Magistrate’s Courts deal with less serious civil and criminal offences. They are referred to as inferior courts of record with broad jurisdiction over common-law actions, cases involving land, issue of warrants, granting of bar and dancehall licences, preliminary inquiries and an inquest into suspicious or unknown causes of death. There is one such court in each of the 14 parishes in the island. The resident magistrate of a parish is also the coroner and conducts preliminary inquiries into criminal matters.
Resident Magistrate’s Courts deal with less serious civil and criminal offences. They are referred to as inferior courts of record with broad jurisdiction over common-law actions, cases involving land, issue of warrants, granting of bar and dancehall licences, preliminary inquiries and an inquest into suspicious or unknown causes of death. There is one such court in each of the 14 parishes in the island. The resident magistrate of a parish is also the coroner and conducts preliminary inquiries into criminal matters.

There are other special courts such as traffic, gun, family, revenue, coroner’s, juvenile
and civil courts.

This refers to the body of employees in any government agency other than the military.
Referred to as civil servants or public servants, these individuals are employed in the public sector in/for a government department or agency.
The civil service executes government decisions and, therefore, plays a vital part in
politics. It is split into a number of departments attached to a government department.
Additionally, there are special bodies under Jamaican law with direct authority over certain
aspects of government business. These bodies are known as statutory bodies and are
autonomous agents within the Government of Jamaica hierarchy. Examples of statutory bodies
are the Jamaica National Heritage Trust and the National Housing Trust.
THE LEGISLATURE

STRUCTURE OF THE LEGISLATIVE
The Parliament of Jamaica is the legislative branch of the Government of Jamaica. It is a
bicameral body, composed of an appointed Senate, also known as the Upper House, and an
elected House of Representatives, also known as the Lower house.
The governor general represents the queen in Parliament, and his role is a formal one. Once a
year, at the official opening of Parliament, he delivers the Throne Speech. The legislature is empowered by the Constitution to amend existing and enact new laws. This arm is also in control of the government’s finances and guides fiscal policy.
The head of state’s role in Parliament, executed through the governor general, is to open and dissolve Parliament and grant royal assent to bills passed in the Houses of Parliament.
SENATE
The Senate is a nominated house made up of 21 senators in Jamaica. Thirteen senators are appointed by the governor general on the advice of the prime minister. The other eight are appointed on the advice of the leader of the opposition. Not more than four ministers can be appointed from the Senate, and they may have portfolio responsibilities.

The Senate usually functions as a review chamber, considering bills passed by the House of Representatives. The Senate may also initiate legislation, except money bills.
HOUSE OF REPRESENTATIVES
The House of Representatives consists of 63 members, elected by single-member constituencies using the first-past-the-post system. The government in power can only exist if it has the support of the majority of the members of the House of Representatives. Most bills are initiated in the House of
Representatives.
THE SPEAKER

The Speaker of the House is formally elected by the members of the House of Representatives from among their number, at the first sitting after each general election or when there is a vacancy. His job includes keeping other members within the rules of the House, and ensuring that the rights of the opposition members are protected and that every member gets a fair hearing.
THE JUDICIARY

The legal system of Jamaica is based on British common law. The administration of justice is carried out through a court system.
The courts of Jamaica are:
The Judicial Committee of the Privy Council, which is the final court of appeal, is based in London, England. It hears appeals on criminal and civil matters from the Jamaican Court of Appeal.

of the Caribbean Community (CARICOM). The CCJ has two core functions: to act as the final appellate court for the CARICOM member states and as an international court ruling on matters relating to the foreign policy coordination of the Revised Treaty of Chaguaramas (2001) that outlines terms of economic cooperation among CARICOM members.

The Court of Appeal consists of the resident of the Court of Appeal, the chief justice (who sits at the invitation of the president) and six judges of the Court of Appeal. A person who is dissatisfied with a decision of one of the other courts, except Petty Sessions, can appeal to this court. Petty Sessions appeals are heard by a judge in chambers or by justices of the peace.

The Supreme Court of Jamaica is responsible for hearing serious civil and criminal matters.


There are other special courts such as traffic, gun, family, revenue, coroner’s, juvenile
and civil courts.
ACTIVITIES
a. State THREE functions of the executive.
b. Identify the components of the executive and state the duties of each group or persons.
c. Give THREE reasons we need an Opposition in Parliament.
d. Suggest THREE ways in which the opposition and the party in power may work together for the good of the country.
e. Make a diagram illustrating the structure of the judicial system in your country.
f. State THREE functions of the judiciary.
g. Suggest THREE ways in which the judiciary strives to protect citizens and explain how successful you think the system is in curbing criminal behaviour in your country.

Comments
Post a Comment